What are the stages involved in planting a vineyard?
- Preparatory work
- Planting the vine stock
- Vine maintenance after planting
If you're planning to plant vines, you'll need to take into account a number of parameters to ensure that the plant flourishes. Follow this E-viti guide to vine planting. On the program : preparing the soil, choosing the vine to plant, the season to plant the vine and its subsequent maintenance.
Preparatory work
Before planting vines, you need to choose a grape variety that is suited to :
- your geographical location,
- your region's climate,
- your PDO or PGI legislation,
- your production project.
You need to prepare the land and soil before planting your vines. Even if Vitis vinifera adapts to many different types of soil, you need to carry out a granulometric analysis to determine its composition. This will enable you to make the right choice of materials and treatments: balancing the pH, adding nutrients, choosing the right rootstock...
Then, to ensure the vine's longevity and optimum production, it's time to uproot the vines, extract the roots and plough deep into the soil. After harvesting and draining the soil, it's essential to respect a resting period before planting the vines.
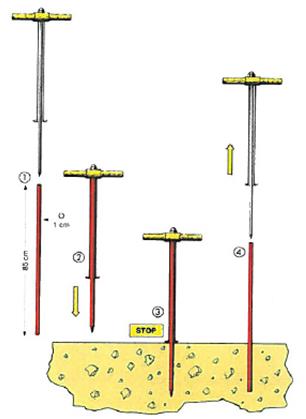
Once the plants have been received, the vines must be removed from their packaging. After checking that they are in good condition, the roots should be shortened to 1 cm in length. This step is not necessary for potted vines.
Planting the vine stock
To plant your vine successfully, you'll need to lay out and staking to define the location and orientation of the vines. Good exposure to the sun and a location protected from the wind enable the vine to photosynthesize, thus developing the grape's sugars and lowering its acidity. South or south-west exposure is ideal for healthy vines.
Mark out the final location of each vine stock on the ground, using stakes or stakes. Make sure you leave enough space for service roads and machinery.
Equip yourself with your vine-planting tools (mechanical planter or manual planter such as the PLAVI). Dig a hole about 30 centimetres deep and 30 centimetres wide. Then install the vine so that the grafting point is a few centimetres above ground level.
To ensure a firm hold for the vine and its development, you'll need to install stakes and ties. Fix them to the ground at a depth that prevents the wind or other disturbing elements from changing the orientation of the vine. Some sites will require a more reliable protection system, such as a planting tubex. Avoid over-tightening the tie.
There are several materials available for the stake, such as metal, wood, fiberglass or bamboo. They have different characteristics in terms of cost, flexibility, recycling...


- Our range of stakes and protection
- Bamboo stakes: available in 3 lengths
- Stakes tube Fenox: for optimal marking of locations. Tubular stakes, strong and flexible, lightweight and reusable. Ideal for staking young vines. Regular, easy and effortless positioning thanks to the planter.
- Fenox planter: for fast, effortless tube stake positioning.
- Galvanized stakes : resistant, perfectly suited to vine planting.

Vine maintenance after planting
Once the vine has been planted, it's time for rigorous and effective maintenance.
First of all, weed growth must be limited. To achieve this, the soil must be aerated and its structure preserved. First of all, it's essential to limit soil dryness. Optimum moisture levels encourage deep root development.
Working the soil is better than weeding, as it is a less aggressive treatment. Among vine planting tools, a weeding knife allows you to do a fairly meticulous job, without risking damaging the vines.
If you use an automatic dethatching machine, try not to let it work too deeply, as this could dry out the roots of the rootstock. At this stage, chemical weeding may be useful, provided you use approved products.
In this first stage of setting, the aim is to encourage root growth. The more the rootstock takes root in the soil, the more productive the vine will be.
When to plant a trellis?
As well as knowing how to plant vines and having the right tools and equipment, you need to know when to plant. This will vary depending on whether the vines are :
Potted vine roots
You can plant these vines all year round, since their roots are already sufficiently developed. They can therefore withstand the relatively extreme temperatures of winter and summer.
Bare vine roots
To be planted after the coldest winter weather, when the soil warms up but the vine is not yet vegetative. Preference should be given to :
- February-June in Mediterranean climates,
- March-June in continental and oceanic climates.
So adapt vine planting to your geographical zone. Especially while the roots are getting stronger and adapting to the soil.
Conclusion
Planting vines is an operation that requires a great deal of attention. Following the steps methodically, and using the right tools, will give you the best chance of success. Some vines will need specific planting systems, such as trellisinga pruning and planting density.